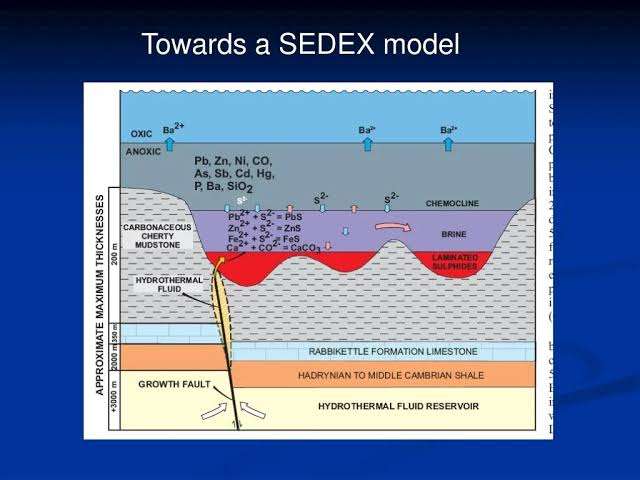
Vein deposits are geological formations characterized by the concentration of minerals within distinct fractures or cracks, creating vein-like structures. These deposits play a significant role in the global mining industry, contributing to the extraction of various valuable metals. Understanding the details of vein deposits involves exploring their types, formation processes, mineralogy, mining methods, economic significance, and notable examples.
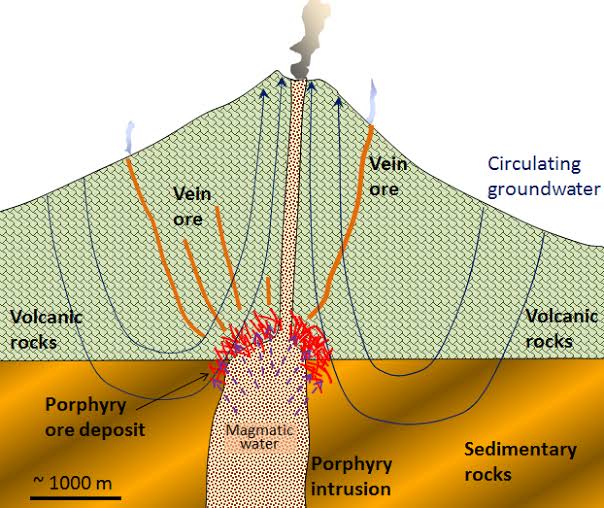
Types of Vein Deposits
Vein deposits are geological formations where minerals are concentrated within distinct fractures or cracks, forming vein-like structures. There are several types of vein deposits, each characterized by the minerals they contain and the geological processes that contribute to their formation.
- Epithermal Vein Deposits: These deposits form at relatively shallow depths and are associated with hot fluids rising from magma chambers. Epithermal veins often contain gold and silver, along with other base metals.
- Mesothermal Vein Deposits: Forming at moderate depths, mesothermal veins are associated with tectonic activity and can contain a variety of metals such as gold, silver, lead, and zinc. The mineralogy of these veins is influenced by the surrounding rock types.
- Hypothermal Vein Deposits: These veins form at greater depths and are associated with high-temperature fluids. They often contain base metals like copper, lead, and zinc, as well as precious metals.
Formation Processes and Mineralogy
Vein deposits are primarily formed through hydrothermal processes, where hot fluids rich in minerals circulate through fractures in the Earth’s crust. The following processes contribute to their formation:
- Magma Intrusion: Magma intrusions heat surrounding rocks, causing them to release mineral-rich fluids.
- Faulting and Fracturing: Tectonic activity creates fractures and faults, providing pathways for mineral-rich fluids to migrate.
- Mineral Precipitation: As the fluids cool, minerals precipitate out, forming veins. Common minerals in vein deposits include quartz, calcite, sulfides (such as pyrite, galena, and sphalerite), and occasionally native metals like gold and silver.
Mining of Vein Deposits
Mining vein deposits involves extracting minerals from the veins using various techniques. The choice of mining method depends on factors such as the depth of the deposit, its geometry, and the economic viability of extraction. Common mining methods include:
- Underground Mining: Vein deposits often extend deep into the Earth, making underground mining the preferred method. Techniques such as shafts and tunnels are employed to access the veins.
- Open-Pit Mining: When vein deposits are near the surface and extend horizontally, open-pit mining may be employed. This method involves removing overburden to access the veins.
Economic Significance and Uses
Vein deposits are economically significant due to the concentration of valuable minerals. The economic significance lies in the extraction of metals used in various industries. Some common uses include:
- Precious Metals: Vein deposits are a significant source of precious metals such as gold and silver, which are used in jewelry, electronics, and investment.
- Base Metals: Deposits containing lead, zinc, and copper contribute to the production of alloys, batteries, and wiring essential for construction and manufacturing.
Notable Vein Deposits
Several notable vein deposits around the world have played a crucial role in the mining industry. Some examples include:
- Comstock Lode (USA): A historic silver and gold deposit in Nevada, USA, known for its immense wealth during the 19th century.
- Witwatersrand Basin (South Africa): Famous for its gold deposits, the Witwatersrand Basin has been a major source of gold production.
- Kalgoorlie Super Pit (Australia): One of the world’s largest open-pit gold mines, located in Western Australia.
In conclusion, vein deposits are diverse geological formations with various types, formation processes, and economic significances. The mining of these deposits has played a crucial role in supplying essential metals for numerous industries worldwide.