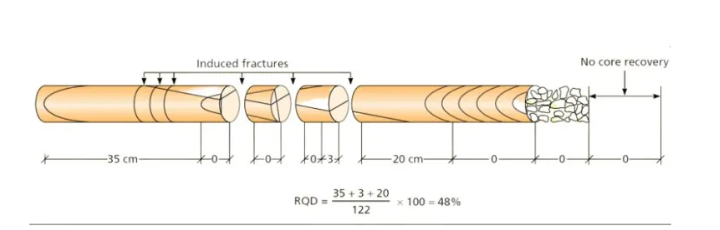
Rock Quality Designation (RQD) is a measure used in geotechnical engineering to assess the quality of rock core samples. It is calculated by measuring the length of intact pieces of rock in a core sample that are longer than 10 cm.
RQD stands for “Rock Quality Designation,” and it is a measure used in geology and geotechnical engineering to assess the quality or degree of intactness of a rock mass or rock core sample. RQD is often used in the context of rock mechanics studies, civil engineering projects, and mining operations. Here’s how RQD is calculated and what it signifies:
To calculate RQD, follow these steps:
- Measure the total length of the core sample in meters (L).
- Determine the total length of intact pieces of rock that are longer than 10 cm (I).
- Calculate the RQD using the formula: RQD = (I / L) x 100

For example, if the core sample is 10 meters long and there are 6 meters of intact pieces of rock longer than 10 cm, the RQD would be:
RQD = (6 / 10) x 100 = 60%
RQD values can range from 0% to 100%, with higher values indicating a higher quality of rock. A value of 90% or above is considered excellent, while values below 50% may indicate poor rock quality. RQD values are used in rock mechanics and geotechnical engineering to evaluate the strength and stability of rock formations
RQD is typically determined by examining a continuous core sample obtained from drilling into a rock formation. It involves measuring the length of the intact or sound rock pieces within the core and expressing it as a percentage of the total length of the core.
The formula for calculating RQD is as follows:
RQD (%) = (Total length of intact or sound rock pieces / Total length of the core) × 100
Interpretation of RQD:
The RQD value is an indicator of the rock mass quality and provides insights into its integrity. Here’s how to interpret RQD values:
- High RQD (e.g., 90% or more): Indicates that the rock core contains a significant amount of intact or sound rock. This suggests good rock quality and stability, which can be favorable for construction or mining.
- Moderate RQD (e.g., 50% to 90%): Suggests a rock core with some fractured or weathered intervals but still contains substantial intact rock. Engineering structures can be built, but additional support or reinforcement might be needed in weaker zones.
- Low RQD (e.g., less than 50%): Indicates a rock core with a high degree of fracturing, weathering, or discontinuities. Such rock masses are often challenging for engineering purposes, and additional measures may be necessary to ensure stability.
RQD is just one of many factors considered in geological and geotechnical assessments. Engineers and geologists use it in conjunction with other rock mass properties, such as joint orientation, spacing, and strength, to make informed decisions about the suitability of a rock formation for various projects, including tunneling, slope stability analysis, and foundation design.

I usedd to be able too find good advice from your content.