Sand Dune Landform: Formation, Types, and Significance
Sand dunes are dynamic landforms created by the interaction of wind, sand, and vegetation. These striking natural features are common in deserts, coastal regions, and even in some semi-arid and arid zones. This article explores every aspect of sand dunes, including their formation, types, ecological significance, and role in shaping landscapes.
What are Sand Dunes?
Sand dunes are mounds or ridges of sand that form due to the transportation and deposition of sand particles by wind (aeolian processes). They are often found in environments where loose, dry, and fine-grained sand is abundant, and vegetation is sparse or absent.
Formation of Sand Dunes
The formation of sand dunes involves three main processes:
- Erosion: Wind erodes loose sand particles from a source area, such as riverbeds, deserts, or beaches.
- Transportation: The wind carries these particles through processes like suspension, saltation, and surface creep.
- Suspension: Fine particles are carried in the air over long distances.
- Saltation: Medium-sized particles are lifted briefly and bounce along the ground.
- Surface Creep: Larger particles are rolled or pushed along the ground by wind.
- Deposition: When the wind loses its energy, sand particles are deposited, forming a dune. Deposition often occurs around an obstacle, like a rock or vegetation, which reduces wind speed.
Factors Affecting Dune Formation
Several factors influence the size, shape, and orientation of sand dunes:
- Wind Strength and Direction: Consistent wind results in the formation of specific dune shapes.
- Availability of Sand: A higher supply of sand leads to larger dunes.
- Vegetation: Sparse vegetation stabilizes dunes, while its absence allows free movement of sand.
- Moisture: Damp sand is less likely to be transported by wind.
Types of Sand Dunes
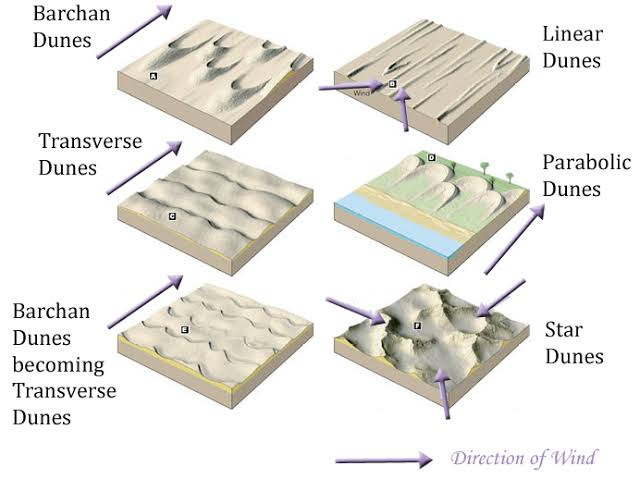
Sand dunes can take various shapes depending on wind patterns and sand availability. Major types include:
1. Barchan Dunes
- Crescent-shaped dunes with horns pointing downwind.
- Form in areas with limited sand and a single dominant wind direction.
- Common in deserts like the Sahara.
2. Transverse Dunes
- Long, linear ridges perpendicular to the prevailing wind.
- Form in areas with abundant sand and consistent wind direction.
3. Linear (Seif) Dunes
- Long, narrow dunes aligned parallel to the wind direction.
- Often formed by bidirectional winds.
4. Star Dunes
- Radial dunes with multiple arms radiating from a central point.
- Form in areas with multidirectional winds, such as the Namib Desert.
5. Parabolic Dunes
- U-shaped dunes with open ends facing upwind.
- Form in coastal areas where vegetation stabilizes the sides of the dune.
6. Coastal Dunes
- Found along shorelines.
- Formed by the interaction of wind and waves transporting sand inland.
Distribution of Sand Dunes
Sand dunes are found in various environments:
- Desert Regions: Sahara (Africa), Gobi (Asia), Thar (India and Pakistan).
- Coastal Areas: Found along beaches worldwide, including the Gulf of Mexico and Australia.
- Inland Basins: Regions like the Great Basin in the United States.
Ecological and Geological Significance
Sand dunes are not just striking landforms but also have immense ecological and geological importance:
1. Habitat Creation
- Coastal dunes support unique ecosystems, including grasses, shrubs, and animal species like birds and insects.
2. Natural Barriers
- Coastal dunes act as natural barriers against storm surges, protecting inland areas from flooding and erosion.
3. Indicators of Wind Patterns
- The orientation and shape of dunes provide insights into prevailing wind directions and climatic conditions.
4. Groundwater Recharge
- Some dunes, like those in deserts, play a role in trapping water, facilitating groundwater recharge.
Human Interaction with Sand Dunes
Humans interact with sand dunes in various ways, including:
- Mining: Sand from dunes is often used in construction and industrial processes.
- Tourism: Dunes like those in Dubai and Namibia attract tourists for activities like sandboarding and safaris.
- Conservation: Efforts are made to stabilize dunes and prevent desertification by planting vegetation and restricting human activities.
Challenges and Threats
Sand dunes face several threats, including:
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels and increased storms can erode coastal dunes.
- Urbanization: Construction near dunes disrupts their natural dynamics.
- Overgrazing and Deforestation: These activities destabilize sand dunes, leading to desertification.
Conservation of Sand Dunes
Conserving sand dunes is critical for maintaining their ecological and geological roles. Strategies include:
- Vegetation Planting: Helps stabilize shifting dunes.
- Controlled Land Use: Restricting development in dune areas.
- Awareness Campaigns: Educating communities about the importance of dunes.
Conclusion
Sand dunes are not only aesthetically captivating but also play a vital role in the environment. From stabilizing ecosystems to serving as natural barriers, their importance cannot be overstated. However, human activities and climate change pose significant challenges to their preservation. A balanced approach involving conservation efforts and sustainable land-use practices is crucial to protect these fascinating landforms for future generations.