Skarn Deposits: Unraveling the Geological Marvel
Skarn deposits, also known as skarns, represent a fascinating geological phenomenon formed through the interaction of hot fluids from intrusive igneous bodies with carbonate-rich sedimentary rocks. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the various types of skarn deposits, their formation process, economic significances, notable examples, and other pertinent details.
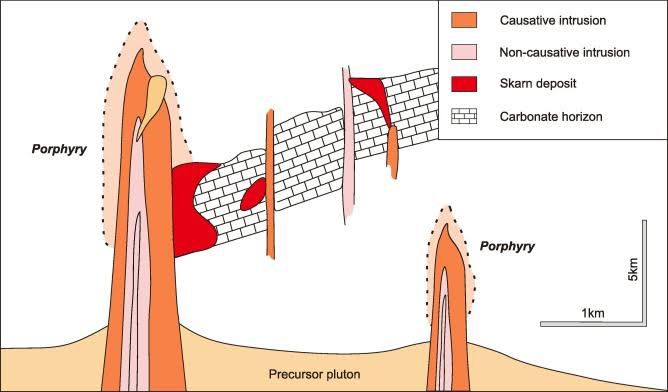
1. Types of Skarn Deposits:
Skarn deposits can be classified into several types based on their dominant mineralogy and geological settings:
- Calcic Skarns: Characterized by the dominance of calcium-rich minerals such as garnet and pyroxene.
- Magnesian Skarns: Enriched in magnesium-rich minerals like forsterite and diopside.
- Iron Skarns: Featuring significant concentrations of iron minerals such as magnetite and hematite.
- Copper Skarns: Rich in copper-bearing minerals like chalcopyrite and bornite.
- Zinc Skarns: Abundant in zinc-bearing minerals such as sphalerite.
2. Formation Process:
Skarn formation typically occurs in the vicinity of intrusive igneous bodies, such as granitic plutons or mafic intrusions, where hot fluids interact with carbonate-rich sedimentary rocks (such as limestone or dolomite). The process involves:
- Intrusion: Molten magma intrudes into the surrounding carbonate rocks, heating them and releasing fluids rich in elements like calcium, iron, magnesium, and sulfur.
- Metasomatism: The hot fluids react with the carbonate rocks, triggering metasomatic alterations and the formation of new minerals, including garnet, pyroxene, and various ore minerals.
- Zoning: Skarn deposits often exhibit zoning patterns, with distinct mineral assemblages and ore types occurring in concentric zones around the intrusive body.
3. Economic Significances:
Skarn deposits are of considerable economic importance due to their enrichment in valuable ore minerals. They serve as sources of various metals, including:
- Copper
- Iron
- Zinc
- Lead
- Gold
- Silver
Skarn-hosted ore bodies can be economically viable targets for mining operations, contributing significantly to global metal production.
4. Notable Examples:
Several notable skarn deposits have been exploited for their mineral wealth, including:
- Bingham Canyon Mine (Utah, USA): One of the world’s largest copper mines, hosted within a copper-bearing skarn deposit.
- Greens Creek Mine (Alaska, USA): A polymetallic mine situated in a zinc-rich skarn deposit, producing silver, gold, zinc, and lead.
- Falun Mine (Sweden): Historically significant for its iron and copper production from iron-skarn and copper-skarn deposits.
5. Other Details:
- Exploration Techniques: Geophysical surveys, geochemical analysis, and geological mapping are commonly employed to identify and delineate skarn deposits.
- Environmental Considerations: Mining activities associated with skarn deposits can have environmental impacts, necessitating responsible mining practices and environmental mitigation measures.
6. Conclusion:
Skarn deposits epitomize the intricate interplay between geological processes and economic mineralization. Their diverse types, formation mechanisms, economic significance, and notable examples underscore their importance in both scientific inquiry and industrial exploitation. As our understanding of skarns continues to evolve, so too does our appreciation for their geological complexity and economic potential.