Placer deposits are natural occurring concentrations of minerals and metals that are found in sedimentary rock formations. These deposits are formed through a series of geological processes that involve the movement, deposition, and alteration of minerals. They are an important source of economic minerals such as gold, silver, copper, lead, and zinc. In this article, we will explore the formation, types, and characteristics of placer deposits, as well as their importance in the global mining industry.
Formation of Placer Deposits:
The formation of placer deposits can be broadly categorized into three main stages:
Weathering and Erosion:
- Weathering is the process by which rocks are broken down into smaller particles by the action of water, wind, and temperature.
- Erosion is the transportation of these weathered particles by water, wind, and ice, which deposit them in various locations.
Enrichment and Concentration:
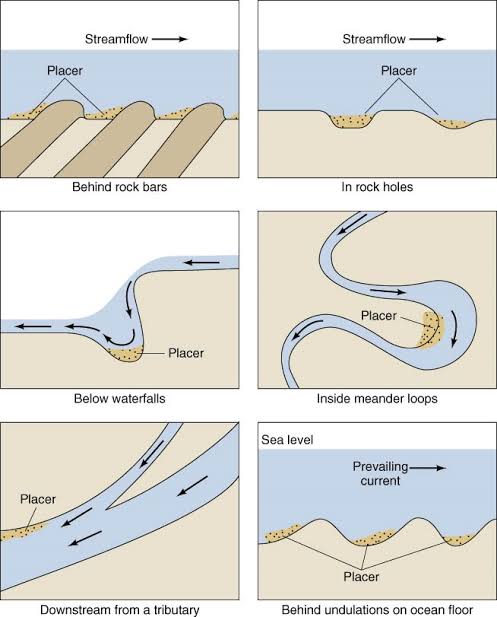
As the eroded particles move through the Earth’s surface, they are subjected to various physical and chemical processes that can enrich them in specific minerals and metals.
These processes include:
- Chemical precipitation: The dissolution of minerals from the rock matrix, followed by their re-deposition as solid concentrates.
- Physical separation: The movement of heavy minerals through the Earth’s crust, which can result in the deposition of concentrated mineral-rich sediments.
Deposition and Burial:
- The enriched particles are deposited in various locations, such as river beds, alluvial fans, and lake basins, where they can be trapped and concentrated further through additional processes.
- Over time, these deposits can be buried under subsequent sedimentary rocks, which can protect and preserve them for future extraction.
Types of Placer Deposits:
There are several types of placer deposits, including:
Alluvial Deposits:
- Formed in river systems where the flow of water carries sediment and minerals, depositing them in fan-like patterns.
- Alluvial deposits are typically rich in gold, copper, and other base metals.
Fluvio-Glacial Deposits:
- Formed by the action of glaciers, which transport and deposit mineral-rich sediments in various locations.
- Fluvio-glacial deposits are rich in gold, silver, copper, and other precious metals.
Marine Placer Deposits:
- Formed in coastal areas where wave action and tidal movements transport sediment, depositing it in accumulation areas.
- Marine placer deposits are rich in gold, silver, and other precious metals.
Desert Placer Deposits:
- Formed in arid regions where wind and water action transport and concentrate minerals, forming desert placer deposits.
- Desert placer deposits are rich in gold, copper, and other base metals.
Characteristics of Placer Deposits:
Placer deposits have several characteristics that make them valuable for mining:
Economic Minerals:
- Placer deposits are rich in economic minerals such as gold, silver, copper, lead, and zinc, which have high market values.
Concentration:
- Placer deposits are typically highly concentrated, meaning that the economic minerals are present in much higher concentrations than in the surrounding rock.
Accessibility:
- Many placer deposits are easily accessible, as they are located in river systems, coastal areas, or desert regions.
Recoverable Reserves:
- Placer deposits often have large recoverable reserves, as they are formed through relatively simple geological processes that can be mined and processed economically.
The Global Importance of Placer Deposits:
Placer deposits play a crucial role in the global mining industry, providing a significant source of economic minerals. Some of the key reasons for the importance of placer deposits include:
Diverse Mineral Resources:
- Placer deposits contain a wide range of minerals and metals, including gold, silver, copper, lead, zinc, and others.
Environmentally Friendly Mining:
- Placer mining is generally considered to be environmentally friendly, as it involves the extraction of minerals from naturally occurring deposits, without significant impacts on the surrounding environment.
Ongoing Discovery and Exploration:
- The geological processes that form placer deposits are ongoing, meaning that new deposits are constantly being formed and discovered.
In conclusion, placer deposits are natural occurring concentrations of minerals and metals that play a vital role in the global mining industry. They are formed through a series of geological processes that involve the movement, deposition, and alteration of minerals, and are rich in economic minerals such as gold, silver, copper, and lead. The importance of placer deposits lies in their diverse mineral resources, environmental friendliness, and ongoing discovery and exploration.