Mississippi Valley-Type (MVT) Deposits: Unveiling the Secrets of Shallow Marine Mineralization
Introduction:
Mississippi Valley-Type (MVT) deposits stand as unique geological formations, characterized by the accumulation of lead and zinc minerals in shallow marine settings. Named after the prolific occurrences in the Mississippi Valley region, these deposits play a vital role in the global production of lead and zinc. In this exploration, we delve into the nature, formation, and economic significance of MVT deposits.
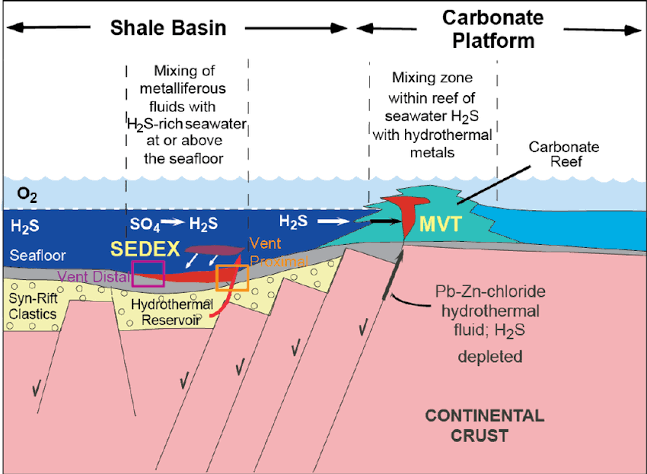
Nature and Composition:
MVT deposits are sedimentary exhalative deposits formed by the precipitation of lead and zinc minerals from hydrothermal fluids. The mineralization typically occurs in limestone and dolostone host rocks, and the deposits are often associated with faults and fractures that serve as conduits for mineral-rich fluids.
Formation Process:
The formation of MVT deposits involves several key processes:
- Hydrothermal Fluids: Mineral-rich hydrothermal fluids, sourced from deep within the Earth, migrate towards the surface. These fluids carry dissolved lead and zinc, among other elements.
- Limestone and Dolostone Host Rocks: The hydrothermal fluids encounter permeable limestone and dolostone rocks. The presence of these carbonate rocks is crucial, as they provide a suitable environment for the precipitation of lead and zinc minerals.
- Chemical Reactions: Upon interaction with the carbonate rocks, chemical reactions occur. The hydrothermal fluids react with the host rocks, leading to the precipitation of lead and zinc sulfide minerals, primarily galena (lead) and sphalerite (zinc). These minerals accumulate in the form of veins or disseminations.
- Faults and Fractures: The mineral-rich fluids are often channeled through faults and fractures in the Earth’s crust. These structural features create pathways for the fluids to move towards the surface and contribute to the concentration of minerals in specific zones.
Geological Characteristics:
- Stratiform and Vein-Type: MVT deposits exhibit both stratiform layers and vein-type occurrences. The stratiform layers are often associated with host carbonate rocks, while veins may form along faults and fractures.
- Shallow Marine Environments: MVT deposits are typically found in shallow marine environments, reflecting their association with carbonate rocks and sedimentary settings.
Economic Significance:
MVT deposits are economically significant due to their high concentrations of lead and zinc. These metals are essential in various industries, including construction, batteries, and manufacturing. The accessibility of MVT deposits in shallow marine settings contributes to their economic viability for mining operations.
Notable Examples:
- Tri-State Mining District (USA): The Tri-State district, encompassing parts of Missouri, Kansas, and Oklahoma, is renowned for its MVT deposits and has been a major historical producer of lead and zinc.
- Pine Point Mine (Canada): Located in the Northwest Territories of Canada, Pine Point was once a significant MVT deposit, contributing substantially to lead and zinc production.
- Iswandiyar Lead-Zinc Deposit (Iran): This deposit in Iran is an example of MVT mineralization occurring in the Middle East.
Conclusion:
Mississippi Valley-Type (MVT) deposits offer a fascinating glimpse into the geological processes that shape shallow marine environments. Their importance as a source of lead and zinc underscores their economic significance and their role in meeting global industrial demands. As we continue to explore and understand the intricacies of these deposits, MVTs remain pivotal in the narrative of Earth’s mineral resources.