Placer gold mining along the Indus River offers a promising opportunity for gold recovery using natural alluvial deposits. In this guide, we explain how to start placer gold mining, develop an efficient processing plant, and optimize recovery using vibrating classifiers, sluice angles, and more.
1. What Is Placer Gold Mining?
Placer gold refers to gold particles that have weathered out of hard rock and accumulated in streambeds or riverbanks. These particles can be recovered economically using gravity-based methods without the need for blasting or chemicals.
2. How to Start Placer Gold Mining
To begin placer gold mining along the Indus River:
Step-by-Step Startup Guide:
- Identify Potential Sites: Use satellite images, sediment maps, and local geology reports.
- Conduct Sample Testing: Pan or sluice-test small samples to estimate gold presence.
- Obtain Permits: Ensure compliance with local mining and environmental laws.
- Assemble Equipment: Prepare a processing plant including classifier, sluice box, and recovery systems.
- Develop Infrastructure: Set up water access, tailings management, and work shelters.
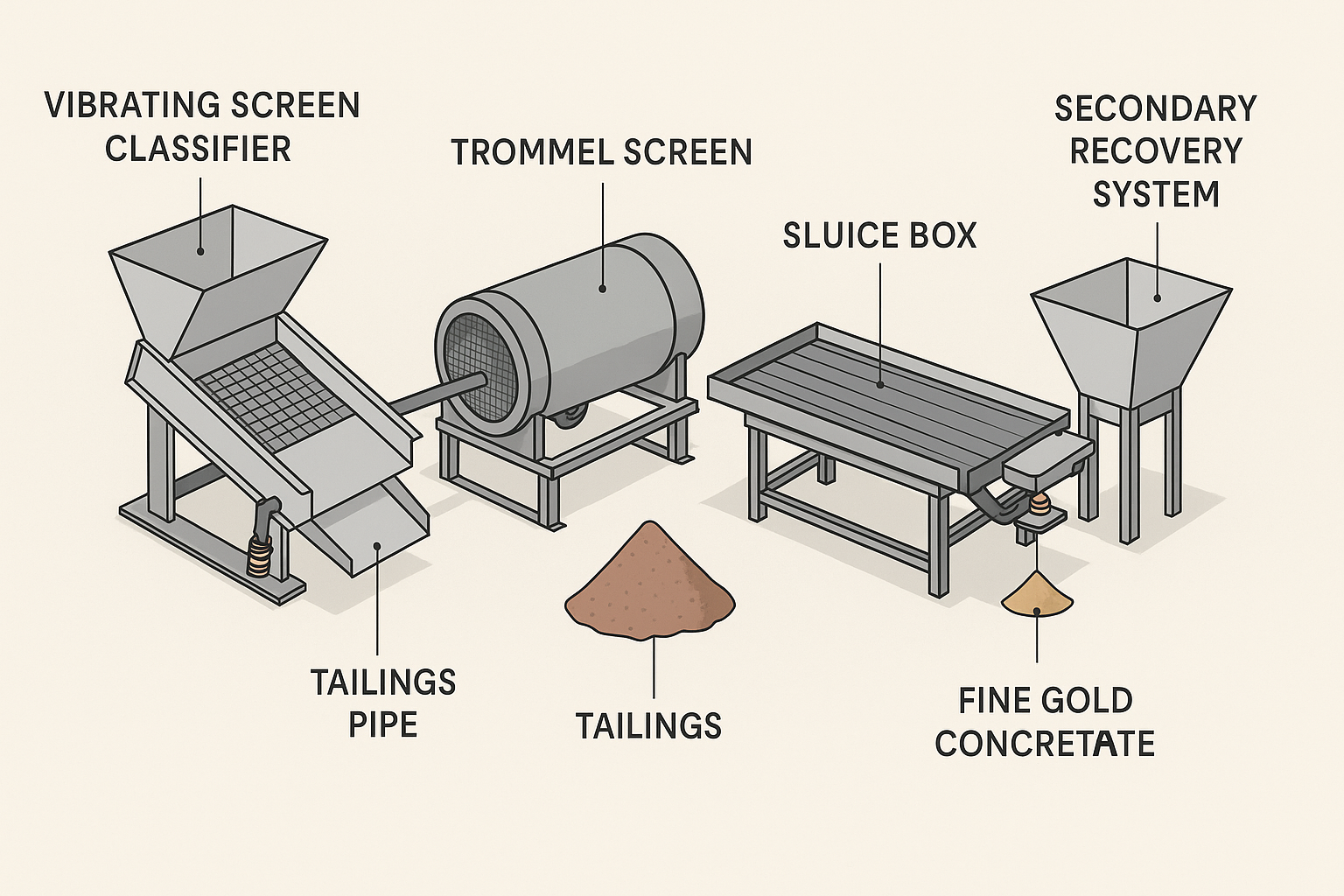
3. Components of a Placer Gold Processing Plant
A. Vibrating Screen Classifier
- Separates oversized rocks and clay.
- Prepares feed for better gold recovery.
B. Trommel Screen
- Rotating cylinder that removes unwanted material.
- Finer gravel and gold pass through to the sluice.
C. Sluice Box
- Uses riffles and mats to trap gold.
- Most cost-effective recovery method for coarse and fine gold.
D. Secondary Recovery System
- Captures fine or “flour” gold that escapes the sluice.
- Includes centrifugal concentrators, shaker tables, or blue bowls.
E. Tailings Pipe and Tailings Area
- Carries waste material (tailings) away from recovery zones.
F. Fine Gold Concentrate
- Final product rich in gold, cleaned manually or refined further.
4. Full Plant Flow Chart
- Raw Material → Vibrating Classifier
- Cleaned Feed → Trommel Screen
- Fine Material → Sluice Box
- Gold-Rich Concentrate → Secondary Recovery
- Tailings → Waste Pipe & Disposal Area
5. Importance of Vibration in Gold Recovery
Vibration is key to improving gold recovery, especially fine particles:
Where to Use Vibration:
- Classifier: Speeds up screening and prevents clogging.
- Sluice Mats: Helps settle fine gold into grooves or carpet.
- Dry Washers: Essential in waterless environments.
Tip: Use a 12V or 24V vibratory motor with a controller to fine-tune the shaking force.
6. Measuring and Setting Sluice Box Angle
The angle of the sluice determines gold recovery efficiency: Sluice Length Standard Angle (1 in/ft) Fine Gold (0.5–0.75 in/ft) 4 feet 4 inches rise 2–3 inches rise
Tools to Use:
- Measuring tape (manual method)
- Bubble level with angle scale
- Mobile inclinometer app
Too steep? Gold washes out.
Too flat? Sluice clogs with black sand.
7. What to Do If Gold Is Found in Tailings?
If you detect gold in tailings:
- Slow down water flow and reduce sluice angle.
- Use finer riffle matting or add secondary concentrators.
- Inspect classifier mesh to ensure it’s not too coarse.
You can reprocess tailings through:
- A fine gold sluice
- Blue bowl or Gold Cube
- Shaker table
8. Optional: DIY Vibrating Classifier Setup
Basic Design:
- Steel or aluminum tray with mesh screen (1/4″ or 1/8″)
- Mount on springs or rubber feet
- Attach 12V vibratory motor under the frame
- Feed water and material from the hopper
Benefit: Classifies faster, improves gold settling downstream.
Conclusion
Starting placer gold mining along the Indus River can be both rewarding and feasible using local materials and smart engineering. By understanding how to set up and optimize each component—from vibrating classifiers to sluice box angles—you can maximize gold recovery and run a sustainable operation.



Leave a comment